What if your LLM could remember an entire textbook without re-reading it every time you asked a question?
Imagine loading a 500-page technical manual into your AI once – and then getting instant, accurate answers from it at any time, without the costly re-reading, re-embedding, or re-searching. Sound like sci-fi? 🛸 Morphik is turning this idea into reality with a new approach called Cache-Augmented Generation (CAG). It’s like giving your LLM a memory upgrade – a big, persistent brain cache so it can remember all the details you fed it, instead of acting like an amnesiac goldfish that has to gulp down the textbook anew for every question. In this post, we’ll explore how CAG works, why it’s a game-changer compared to traditional RAG pipelines, and how you can try Morphik’s implementation yourself. Get ready for some fun analogies, a bit of technical deep-dive, and a demo code snippet. By the end, you might wonder why you ever let your poor AI reread War and Peace a hundred times a day. 😉The Problem with Traditional RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
RAG’s chunk-embed-retrieve loop adds latency, context bloat, and complexity – and it can still fail if the right chunk isn’t retrieved.
- Repeated Reading = Latency: Every single query incurs extra steps – embedding the user query, vector search, and then the LLM has to digest the retrieved text chunks. This real-time retrieval introduces significant latency. It’s like asking a question and making the AI run to the library to fetch reference pages each time before answering.
- Context Window Bloat: Those retrieved chunks take up precious space in the prompt. If you pull in, say, four 500-token passages for each query, that’s 2 000 tokens of your context window gone. In RAG, it’s common to hit context size limits or pay huge token costs because you’re repeatedly shoving documents into the prompt.
- Potential Errors in Retrieval: The pipeline can fail if the vector search misses a relevant chunk or grabs an irrelevant one. If the answer was in a section that wasn’t retrieved, your LLM won’t magically know it.
- Complexity & Maintenance: A full RAG stack is a bit of an engineering circus 🎪. You have to maintain a vector database, an embedding model, possibly a retriever/reranker, handle chunking logic, etc. More moving parts means more chances for something to break. As one analysis put it, RAG’s integration of multiple components increases system complexity and requires careful tuning.
Cache-Augmented Generation: Giving Your LLM a Memory Upgrade
Preload the full document once, save the transformer’s key-value cache, and reuse it for all future queries.
past_key_values that normally store attention states from previous tokens) to store an entire knowledge base inside the model’s context. Think of it as building a cache layer for the brain of your model.
- One-Time Ingestion into the KV Cache: You feed the entire document or set of documents to the LLM once as a massive initial prompt. The model processes this just like it would with a long context, except now we save the model’s internal state (the key-value pairs from each transformer layer) after ingesting the docs.
- Blazing-Fast Queries from Memory: When a user query comes in, we don’t stuff the documents into the prompt at all. We simply reload the cached state into the model’s transformer stack and feed in the new question tokens.
- Reuse, Updates, and Multi-turn: The cached knowledge can be reused across any number of queries – your LLM now has the “textbook in mind” permanently for that session. You can append new docs with another one-time evaluation step.
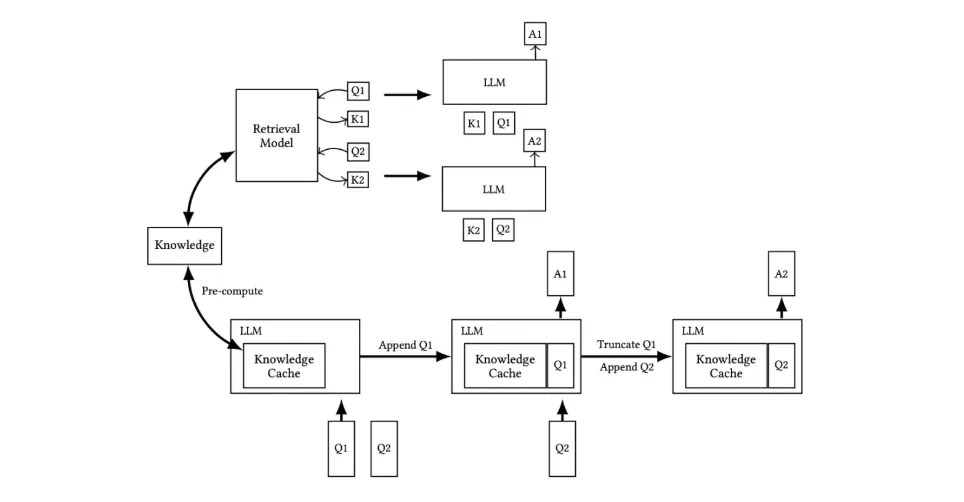 Figure 1 – Traditional RAG (top) vs Cache-Augmented Generation (bottom). In Morphik, the “Knowledge Cache” is the serialized transformer key-value state.
Figure 1 – Traditional RAG (top) vs Cache-Augmented Generation (bottom). In Morphik, the “Knowledge Cache” is the serialized transformer key-value state.
Why Cache-Augmented Generation Is a Big Deal
- Speed, Speed, Speed: Eliminating retrieval can reduce end-to-end latency by ~40 % in benchmarks on static datasets.
- Reduced Token Costs: Pay the document tokens once; each subsequent query might only cost ~50 tokens.
- No Lost Context: The model can synthesize info across the entire document.
- Simpler Infrastructure: No vector DB or rerankers – just the LLM and a cache.
- Multi-turn Consistency: Because the cache persists, conversations naturally stay in sync.
If your knowledge base is huge (millions of docs) or changes every hour, stick with RAG or use a hybrid strategy.
Cache-Augmented Generation in Action (Morphik Demo)
1
Install Morphik
2
Ingest Your Document
3
Create the Cache
4
Query Away – Lightning Fast!
RAG vs CAG Cheat Sheet
| Aspect | Retrieval-Augmented (RAG) | Cache-Augmented (CAG) |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Vector DB + retriever + LLM | Just LLM + cache |
| Per-Query Latency | Embed + search + LLM | LLM only |
| Token Cost / Query | High (docs repeated) | Low (docs once) |
| Best For | Huge / dynamic KBs | Static or medium KBs that fit context |
| Answer Quality Risk | Missed retrievals | Full context inside model |
| Infra Complexity | Many moving parts | Minimal |
| Data Updates | Naturally incremental | Cache must be invalidated / rebuilt |
Try It Yourself
Installing Morphik is a one-liner, and the SDK hides all the complexity:Future roadmap: persistent caches, multi-document graphs, smart eviction, and hybrid RAG-CAG for ever-fresher knowledge stores.Ready to give your LLM a memory boost? Try Morphik today and let your AI learn once, answer forever! 🚀

